Diode Description
fig.1 - Diodes
Diode, electronic device that allows the passage of current in only one direction. How things evolved … The first such devices were vacuum-tube diodes, consisting of an evacuated glass or steel envelope containing two electrodes - a cathode and an anode. Because electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to anode, the vacuum-tube diode could be used as a rectifier . The diodes most commonly used in electronic circuits today are semiconductor diodes. The simplest of these, the germanium point-contact diode, dates from the early days of radio, when the received radio signal was detected by means of a germanium crystal and a fine, pointed wire that rested on it. In modern germanium (or silicon) point-contact diodes, the wire and a tiny crystal plate are mounted inside a small glass tube and connected to two wires that are fused into the ends of the tube.





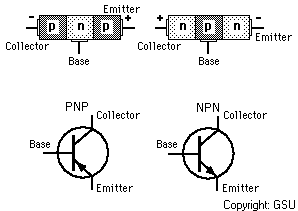 A junction transistor consists of a thin piece of one type of semiconductor material between two thicker layers of the opposite type. For example, if the middle layer is p-type, the outside layers must be n-type. Such a transistor is an NPN transistor. One of the outside layers is called the emitter, and the other is known as the collector. The middle layer is the base. The places where the emitter joins the base and the base joins the collector are called junctions.
A junction transistor consists of a thin piece of one type of semiconductor material between two thicker layers of the opposite type. For example, if the middle layer is p-type, the outside layers must be n-type. Such a transistor is an NPN transistor. One of the outside layers is called the emitter, and the other is known as the collector. The middle layer is the base. The places where the emitter joins the base and the base joins the collector are called junctions.



